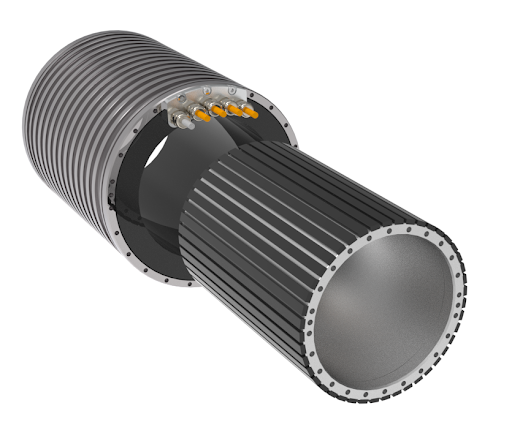
A direct-drive motor is any motor — rotary or linear — in which the load is connected directly to the motor, without mechanical transmission elements such as gearboxes or belt and pulley systems. In other words, the motor directly drives the load.
Direct drive rotary motors
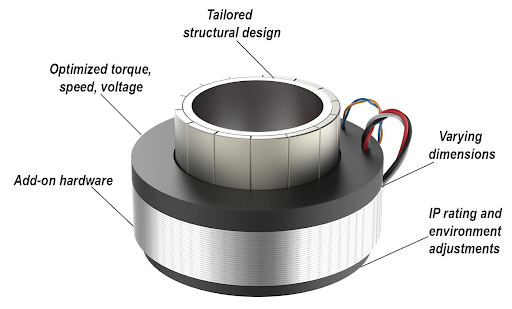
Rotary direct drive motors are often referred to as torque motors because of their ability to produce high torque at low speeds, even when stalled. Torque motors tend to be brushless, permanent magnet synchronous motors — much like a traditional servo motor, but with a large number of poles. They’re often provided as frameless designs, meaning they don’t include a housing, bearings, or feedback device, with these components being purchased separately and integrated by the user.
Direct drive motor benefits and applications
Regardless of its design — rotary or linear, flat or tubular, iron core or ironless — a direct drive motor has the benefit of eliminating mechanical components that can introduce backlash or compliance and degrade positioning accuracy and repeatability. The elimination of mechanical connections also reduces load inertia and allows more dynamic moves — i.e. higher acceleration and deceleration rates with heavier loads — with less overshoot and oscillation. Direct drive motors also have lower noise production than conventional motors, which is important for noise-sensitive applications, like those in the medical and laboratory industries.

Our state of the art machining and assembly sections ensures every motor is dimensionally precise. Our winding section ensures every copper conductor is optimal in our motors. The Vacuum Impregnation and Encapsulation units installed offers electrical and mechanical robustness.
Rotary direct drive motor are used for:
Without additional transmission elements, direct-drive motors tend to be more compact than traditional motors, making them easier to integrate into machines and systems with tight spaces. And with fewer mechanical components (often, the only wear components are linear guides), maintenance is reduced and the mean time between failures (MTBF) is increased.
Rotary direct drive motors are used to drive goniometers, gimbals, rotary tables, and SCARA and 6-axis robot arms. Many designs have a center bore, which allows electrical cables and pneumatic lines to be routed through the center of the motor.
Author: Nimble Electric Experts
This blog was a collaborative effort among a team of experts here at Nimble Electric, including engineers, customer service and design experts. Wherever you are in your project, we’re here to help.